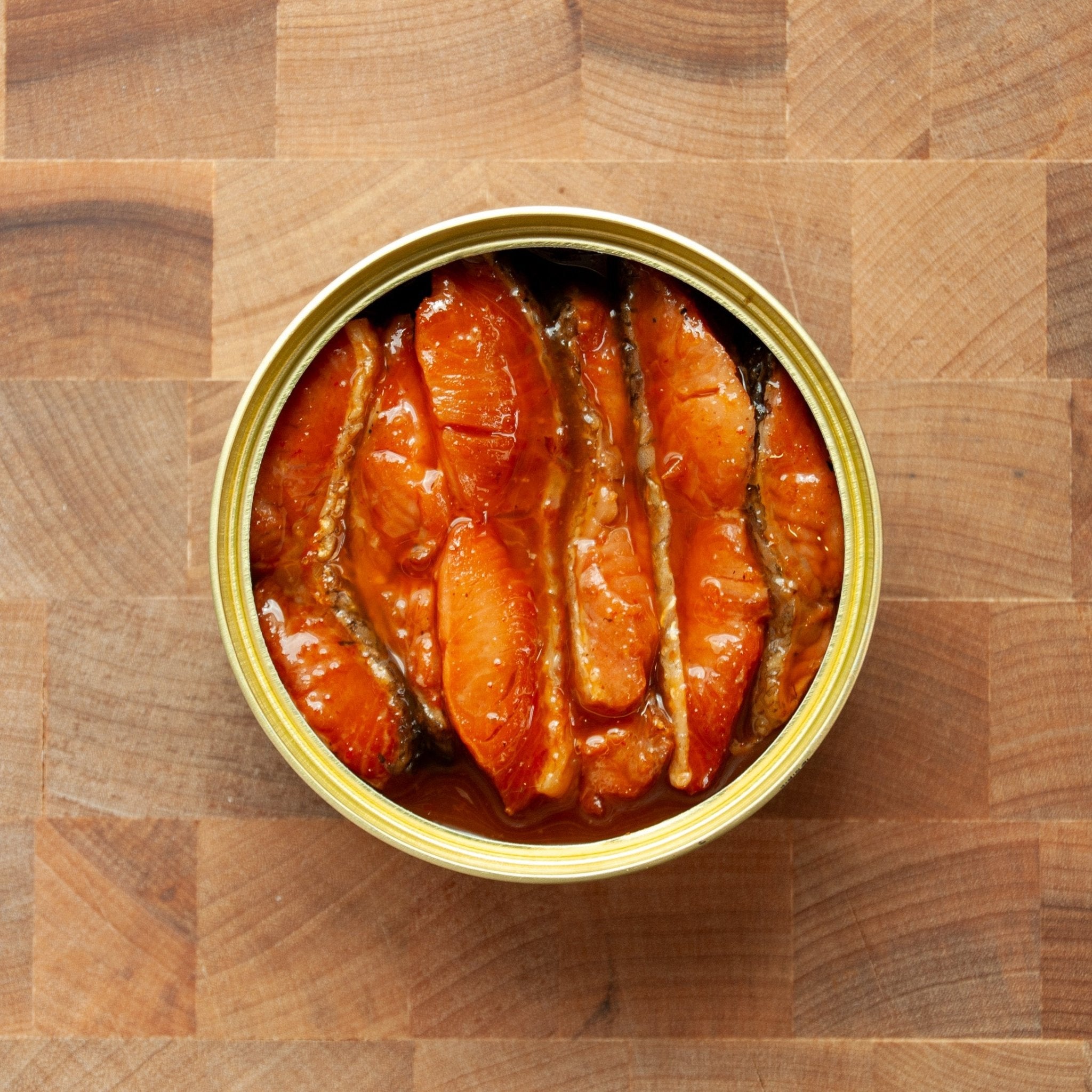
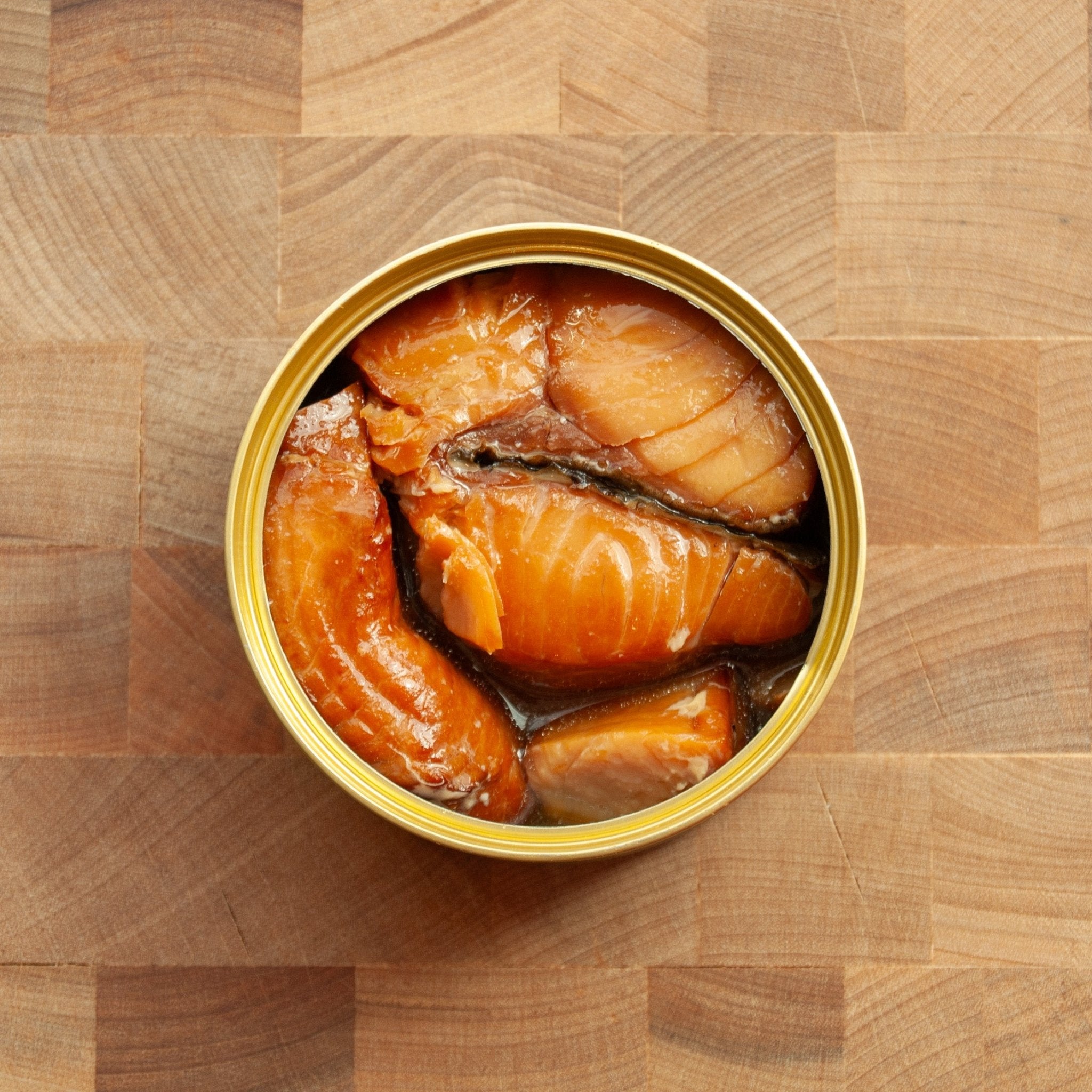
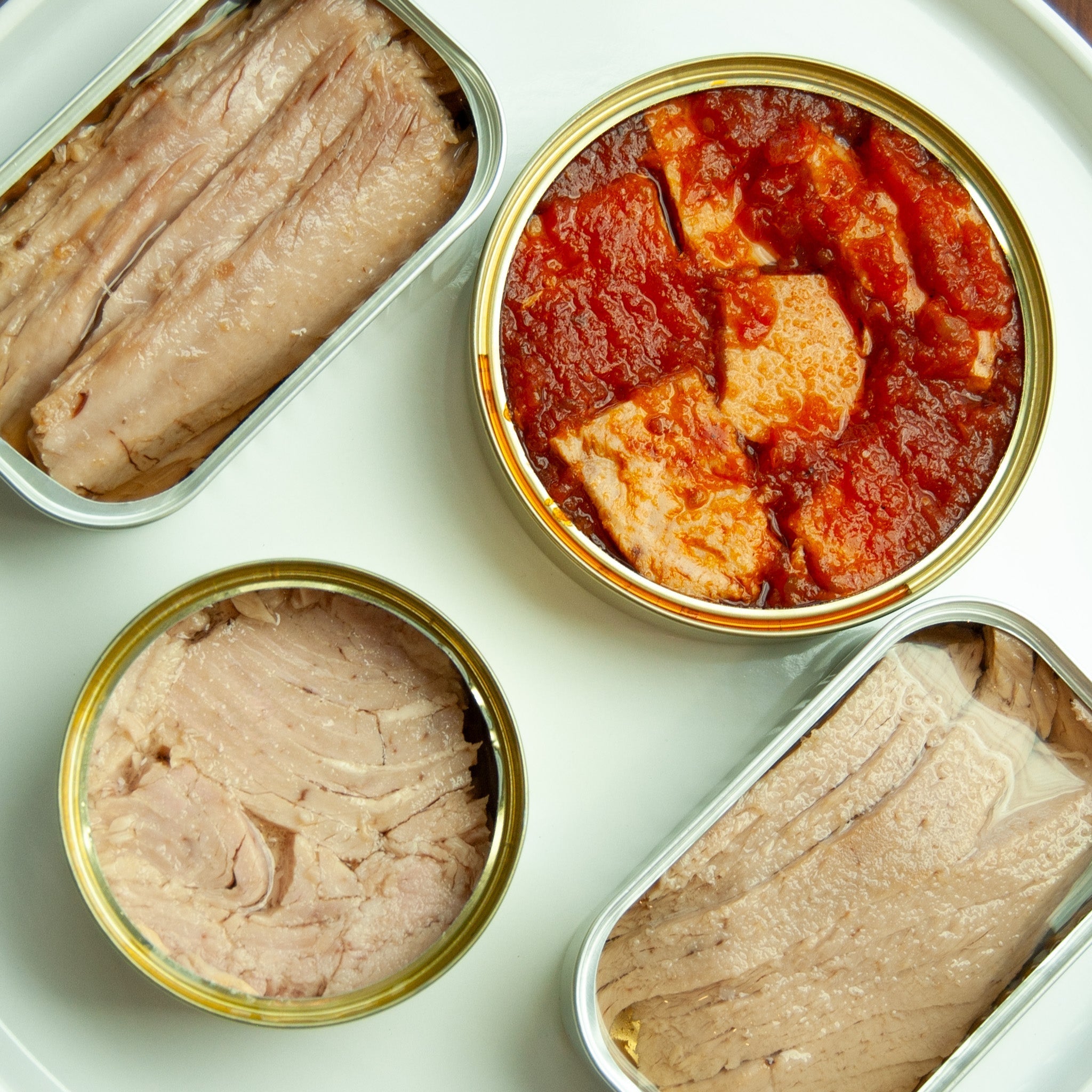
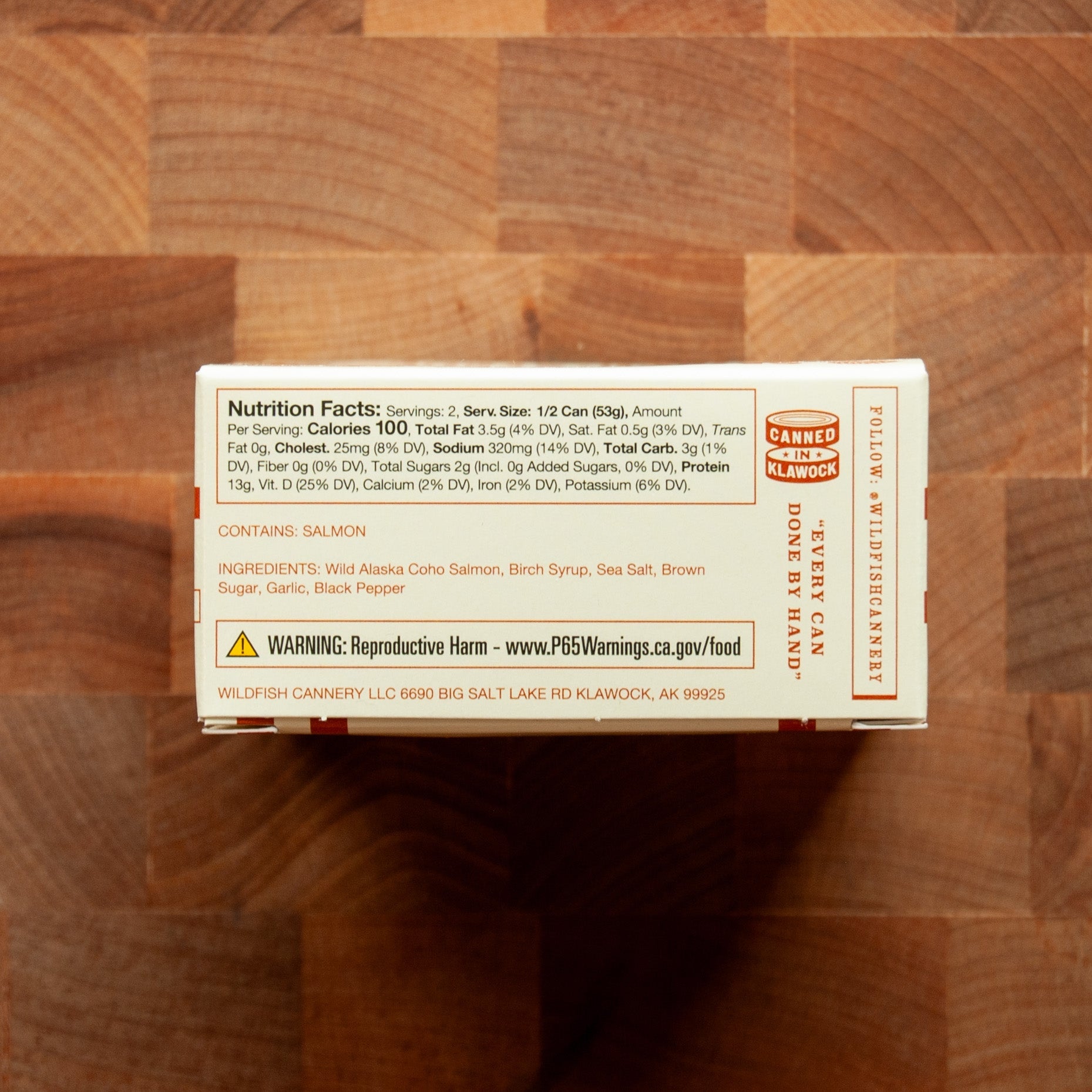
According to the USDA FoodData Central and the NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, canned salmon is an excellent source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA), vitamin D, vitamin B12, selenium, and other essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being.
High-quality protein powerhouse. Canned salmon provides complete protein containing all essential amino acids needed for muscle maintenance, tissue repair, and overall body function. A typical serving delivers 20-25 grams of easily digestible protein, making it an excellent choice for meeting daily protein requirements.
Omega-3 fatty acids for heart and brain health. The EPA and DHA omega-3s found in salmon support cardiovascular function, brain health, and help reduce inflammation throughout the body. These beneficial fats are particularly important since the body cannot produce them on its own.
Exceptional vitamin D content. Salmon is one of the few food sources naturally rich in vitamin D, which supports bone health, immune function, and calcium absorption. This is especially valuable since many people have insufficient vitamin D intake from other dietary sources.
Essential micronutrients. Canned salmon provides substantial amounts of vitamin B12 for nerve function and red blood cell formation, plus selenium—a powerful antioxidant that supports thyroid function and cellular protection against oxidative stress.
Additional nutritional benefits include phosphorus for bone and teeth health, potassium for heart function and blood pressure regulation, and various B vitamins that support energy metabolism.
Convenience maintains nutritional integrity, making these benefits easily accessible for regular inclusion in a healthy diet.